Cuando los profesionales del Business Intelligence (BI) oímos hablar de Big Data existe una cuestión que nos suele venir a la cabeza casi de forma natural ¿Es posible usar Big Data para el desarrollo de aplicaciones de BI típicas como el análisis OLAP o la generación de informes?
A continuación, si la respuesta es afirmativa, con seguridad nos surgirán algunas dudas más:
- Posibilidades de conexión con las herramientas de BI. Por ejemplo con Pentaho, la suite BI Open Source más conocida y líder del mercado
- Rendimiento con aplicaciones de generación de informes y OLAP
- Carga de datos relacionales, procesos de ETL con Big Data, automatización de los procesos…
Para intentar dar respuesta a algunas de las cuestiones anteriores, hemos llevado a cabo un conjunto de pruebas para el desarrollo de aplicaciones BI haciendo uso del binomio Hadoop – Pentaho.
La prueba ha consistido en replicar un Data Warehouse generado en un proyecto real sobre una BBDD Oracle y con una alta volumetría, a un nuevo Data Warehouse en el clúster Hadoop usando la herramienta Apache Hive.
Gracias a la conexión JDBC, conectaremos Hive con las aplicaciones disponibles en la suite Pentaho para evaluar la viabilidad de la generación de informes o reporting con Big Data, siendo esta una de las aplicaciones BI más demandadas en la actualidad por las empresas.
Para llevar a cabo la prueba hemos usado las últimas versiones 6.X de las herramientas de Pentaho y disponemos de un clúster Hadoop con las siguientes características:
· 2 máquinas o hosts
· 2 procesadores por máquina (total 4)
· 16 Gb Ram por máquina (total 32 Gb)
Generación de informes
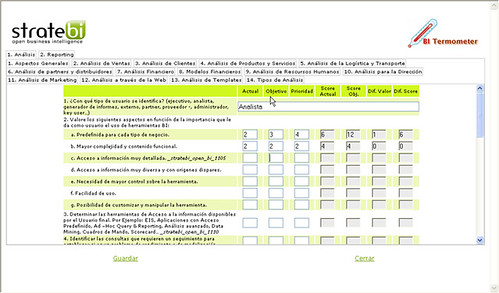
En la siguiente imagen puede verse la arquitectura de la aplicación BI desarrollada:
Para la carga de las tablas del DW de Oracle en Hadoop hemos usado tanto Sqoop como Pentaho Data Integration, gracias a la integración de esta última con HDFS y Sqoop.
Tras esto, para la creación del Data Warehouse en Hadoop hemos usado la herramienta Apache Hive. Esta herramienta soporta consultas en lenguaje SQL y usa como almacenamiento el sistema de archivos distribuido de Hadoop HDFS. Además, recientemente se ha incorporado en la distribución Hortonworks el nuevo motor de ejecución Apache Tez, que mejora en gran medida el rendimiento de Hive haciendo uso intensivo de la memoria RAM del clúster y evitando el uso de IO a disco siempre que sea posible.
Por último, hemos usado la conexión JDBC disponible en Hive para conectar con las siguientes aplicaciones de la suite Pentaho, con el objetivo de dar soporte a la generación de informes sobre el Data Warehouse creado Hive:
* Pentaho Reporting Designer: Usada para la generación de informes estáticos y parametrizables. Para las pruebas hemos creado 3 informes con consultas de distinta complejidad.
* Pentaho Metadata Editor: Creación de un modelo de metadatos que es usado por aplicaciones como STReport para la generación de informes AdHoc, herramienta incluida en la suite Lince BI, desarrollada por el equipo de StrateBI a partir de Saiku Reporting. Con STReport generaremos 3 informes con consultas similares a las de los 3 informes estáticos generados con Pentaho Reporting Designer.
* Pentaho BA Analytics (Servidor de BI): Servidor de BI de Pentaho, donde ejecutaremos los informes creados con Pentaho Reporting Designer y crearemos nuevos informes sobre el modelo de metadatos usando la herramienta STReport
Dado que los entornos Big Data están preparados para procesar volúmenes de datos mucho más grandes que los de nuestro DW de ejemplo, hemos creado dos tablas de hechos adicionales a la original de 1.240.361 filas, las cuales tienen 5.161.444 filas (x4) y 25.807.220 (x20) respectivamente. De esta forma hemos creado versiones de los 6 informes (3 estáticos con PRD y 3 adhoc con PME + STReport) que se ejecutan sobre las 3 tablas de hechos de distinta volumétrica.
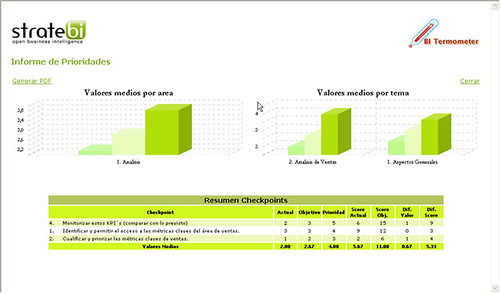
Tras la ejecución, en la siguiente tabla se muestran los tiempos de generación medidos:
Conclusiones
Esta prueba nos demuestra que es posible la generación de informes sobre datos que están almacenados en una plataforma Big Data como Apache Hadoop, gracias a las capacidades de la herramienta Apache Hive y su conectividad JDBC.
También hemos comprobado como las herramientas de la suite Pentaho, gracias a su conectividad con Hadoop, son el complemento ideal para el desarrollo de aplicaciones BI que hacen uso del Big Data.
No obstante es necesario tener en cuenta los tiempos de respuesta en la generación de informes, los cuales hacen que la generación de informes sobre Hive sea recomendada en casos los que el tiempo respuesta instantánea no sea un requisito indispensable. A cambio, obtenemos la posibilidad de generar informes sobre datos de tipo Big Data (Volumen, Variedad y Velocidad).
En cualquier caso, nuestro clúster de pruebas tiene unas prestaciones muy reducidas, siendo habitual el despliegue de clúster que cuentan con más 5 máquinas y un cantidad de memoria RAM en conjunto superior a los 100 Gb. Es precisamente el uso intensivo de la RAM por Apache Hive (sobre el motor de ejecución Tez), lo que seguramente está penalizando nuestros tiempos en respuesta en más de 10-15 segundos.
Dado que existen más herramientas y aplicaciones BI susceptibles de ser desarrollados con la tecnología Big Data, en pruebas posteriores nos proponemos comprobar las capacidades de Apache Impala para la generación de informes en una distribución de Cloudera o el análisis OLAP usando el novedoso Kylin sobre Hadoop
Esperamos que os sea útil
·